너비 우선 검색 우선-첫 탐색, FSO) 이다
- BFS(Breadth-First Search)는 그래프의 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나로, 루트 노드에서 시작하여 모든 이웃 노드를 먼저 검색한 다음 이 이웃 노드를 시작점으로 모든 이웃 노드를 다시 방문합니다.
BFS의 원리
BFS는 큐 데이터 구조를 사용하여 구현할 수 있습니다. 시작 노드가 먼저 대기하고 해당 노드에 인접한 모든 노드가 대기열에 추가됩니다. 그런 다음 노드를 하나씩 대기열에서 빼고 인접한 노드를 다시 대기열에 추가합니다. 대기열이 비워질 때까지 이 과정을 반복합니다. 대기열을 사용하기 때문에 선입 선출을 너비 우선 검색이라고 합니다.
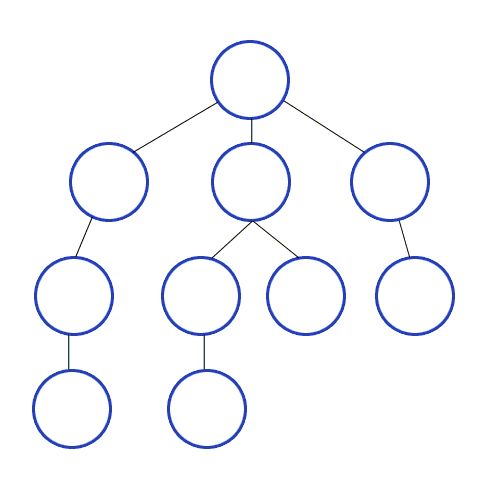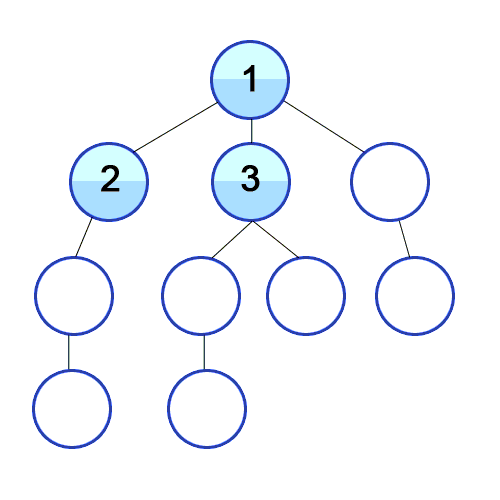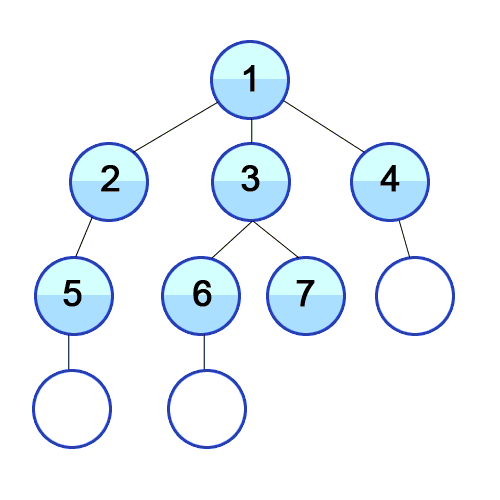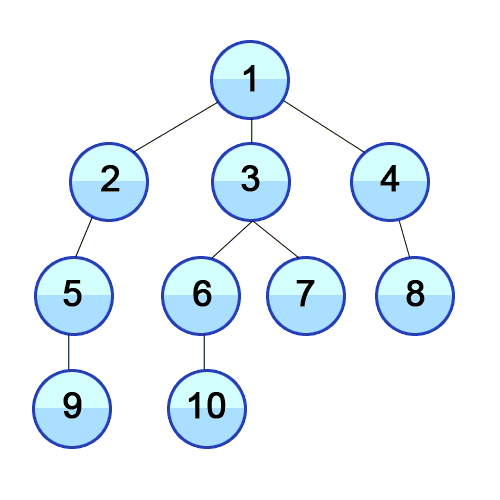
BFS는 종종 최단 경로 등을 찾는 데 사용됩니다. 미로 찾기와 같은 문제에서도 사용할 수 있습니다. 단점은 검색할 노드 수가 많기 때문에 BFS가 깊이 우선 검색(DFS)보다 느리다는 것입니다.
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
- C 언어
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct tagNode
{
ElementType Data;
} Node;
typedef struct tagCircularQueue
{
int Capacity;
int Front;
int Rear;
Node* Nodes;
} CircularQueue;
void CQ_CreateQueue(CircularQueue** Queue, int Capacity);
void CQ_DestroyQueue(CircularQueue* Queue);
void CQ_Enqueue(CircularQueue* Queue, ElementType Data);
ElementType CQ_Dequeue(CircularQueue* Queue);
int CQ_GetSize(CircularQueue* Queue);
int CQ_IsEmpty(CircularQueue* Queue);
int CQ_IsFull(CircularQueue* Queue);
int CQ_Front(CircularQueue* Queue);
int CQ_Back(CircularQueue* Queue);
void CQ_CreateQueue(CircularQueue** Queue, int Capacity)
{
// 큐를 자유 저장소에 생성
(*Queue) = (CircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(CircularQueue));
// 입력된 Capacity+1 만큼의 노드를 자유 저장소에 생성
(*Queue)->Nodes = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node) * (Capacity + 1));
(*Queue)->Capacity = Capacity;
(*Queue)->Front = 0;
(*Queue)->Rear = 0;
}
void CQ_DestroyQueue(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
free(Queue->Nodes);
free(Queue);
}
void CQ_Enqueue(CircularQueue* Queue, ElementType Data)
{
int Position = 0;
if (Queue->Rear == Queue->Capacity)
{
Position = Queue->Rear;
Queue->Rear = 0;
}
else
Position = Queue->Rear++;
Queue->Nodes(Position).Data = Data;
}
ElementType CQ_Dequeue(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
int Position = Queue->Front;
if (Queue->Front == Queue->Capacity)
Queue->Front = 0;
else
Queue->Front++;
return Queue->Nodes(Position).Data;
}
int CQ_GetSize(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
if (Queue->Front <= Queue->Rear)
return Queue->Rear - Queue->Front;
else
return Queue->Rear + (Queue->Capacity - Queue->Front) + 1;
}
int CQ_IsEmpty(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
return (Queue->Front == Queue->Rear);
}
int CQ_IsFull(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
if (Queue->Front < Queue->Rear)
return (Queue->Rear - Queue->Front) == Queue->Capacity;
else
return (Queue->Rear + 1) == Queue->Front;
}
int CQ_Front(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
return Queue->Nodes(Queue->Front).Data;
}
int CQ_Back(CircularQueue* Queue)
{
return Queue->Nodes(Queue->Rear - 1).Data;
}
int n = 5;
int visited(100);
int list(100)(100);
void bfs(int v) {
CircularQueue* queue = NULL;
CQ_CreateQueue(&queue, 5);
CQ_Enqueue(queue,v);
visited(v) = true;
printf("%d\n", v);
while (CQ_IsEmpty(queue)) {
int temp = CQ_Dequeue(queue);
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (list(temp)(i) && !visited(i)) {
CQ_Enqueue(queue, i);
printf("%d\n", i);
}
}
}
}
int main(void) {
n = 5;
list(0)(1) = 1;
list(0)(2) = 1;
list(1)(0) = 1;
list(1)(2) = 1;
list(1)(3) = 1;
list(1)(4) = 1;
list(2)(0) = 1;
list(2)(1) = 1;
list(3)(1) = 1;
list(4)(1) = 1;
//노드 방문
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited(i)) {
bfs(i);
}
}
}- 씨#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace yongyong2
{
internal class Program
{
static int N;
static int(,) Map;
static bool() dfsbool;
static bool() bfsbool;
static void Main(string() args)
{
string() input1 = Console.ReadLine().Split();
N = int.Parse(input1(0));
int M = int.Parse(input1(1));
int V = int.Parse(input1(2));
Map = new int(N + 1, N + 1);
bfsbool = new bool(N + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
string() input2 = Console.ReadLine().Split();
int temps = int.Parse(input2(0));
int tempe = int.Parse(input2(1));
Map(temps, tempe) = 1;
Map(tempe, temps) = 1;
}
BFS(N, V);
}
public static void BFS(int N, int V)
{
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
queue.Enqueue(V);
bfsbool(V) = true;
Console.Write(V + " ");
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
int temp = queue.Dequeue();
for (int i = 1; i < N + 1; i++)
{
if (Map(temp, i) == 1 && bfsbool(i) == false)
{
queue.Enqueue(i);
Console.Write(i + " ");
bfsbool(i) = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}예제 문제
(C#) 백준 #1260: DFS 및 BFS
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260 #1260: DFS와 BFS의 첫 번째 줄에서 노드 개수 N(1≤N≤1,000), 엣지 개수 M(1≤M≤10,000) , 검색을 시작할 정점. 숫자 V가 주어진다. 다음 M 라인은 가장자리로 연결됩니다.
yongongye.tistory.com
(C#) 백준 #24444: 알고리즘 수업 – 너비 우선 검색 1 https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/24444 #24444: Algorithm Lesson – Breadth-First Search 1 첫 번째 줄에서 꼭지점의 수는 N(5 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)이고 모서리의 수는 M( 1 ≤ M ≤ 200,000), 시작 노드 R(1 ≤ R ≤ N)이 주어집니다. 가장 가까운 M 라인으로 이동 yongongye.tistory.com
